The internet is a complex ecosystem in which to operate, with many different protocols and technologies vying for dominance as the number of websites and users grow. This increase in traffic has led to congestion, as internet infrastructure struggles to meet demand. Thankfully, many technologies have been developed to boost the performance of websites and ensure data is delivered quickly and efficiently around the globe.
When considering how well, or badly, a website is performing when trying to connect to data online, there are a number of different reasons to consider. As well as the performance of your own ISP and device, it is important to remember that when you request a specific piece of data online, your request is routed through many different intermediaries and networks before it reaches your screen.
How One AI-Driven Media Platform Cut EBS Costs for AWS ASGs by 48%

This is where Traceroute comes in. It is a technology that is included within operating systems, and its beginnings can be traced back to UNIX in the 1970s. Now with a presence on Microsoft and Apple operating systems, Traceroute provides a method, via a command line, to measure the internet connection between all the servers on your data request’s path, analysing packet loss and latency rates.
How does Traceroute work?
Traceroute works by determining the entire route that data makes from its origin server to your screen once it has been requested. By simply inputting the IP or web address of the target machine, it provides an insight into the path taken, and therefore the number of hops and different networks that it must pass through. The different hops are each displayed on screen, with their IP address listed and a ping measurement. By showing the network delay on each intermediary, we are able to see where bottlenecks are occurring and which the weakest link in the data chain is, highlighting any problems between the origin and destination machines.
Traceroute is able to do this by sending packets of data using the same method as simple ping requests – the ICMP protocol. Each packet contains a time-to-live (TTL) function, which limits the life of the data packet. The first packet has a TTL of 1, the second has a TTL of 2, and so forth, with each hop along the network reducing the TTL of a packet by one. The reason for this is that, as the TTL for each packet reaches 0, the server that it is currently at will send an error message along with a response time. This method therefore allows an error message to be displayed from each server along the route, providing the insight required.
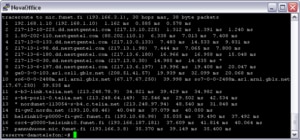
Using Traceroute
There are a few different ways of using Traceroute, depending on your operating system. Windows users must open a command line window (preferably with administrator privileges) and enter the following text:
tracert domainname.com
Apple OS and Linux users, on the other hand, must use the following text:
traceroute domainname.com
Traceroute is an ideal method for identifying weak links on the network chain. Thanks to its ease of use and the fact that it is built into all mainstream operating systems by default, it is easy to take advantage of its power and ensure your data is travelling by the best means possible.







