It wasn’t so long ago that managing and securing enterprise networks was a lot simpler.
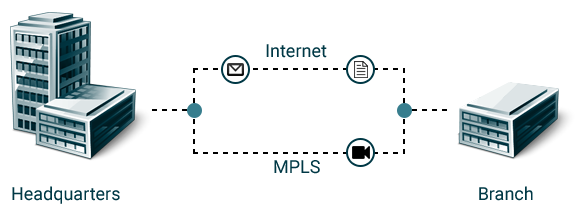
The wide area network (WAN) of choice was MPLS. The only users were those in fixed locations and the only corporate applications were those housed on company premises. Security meant anti-virus software on endpoints and a firewall protecting the company from the dangerous and wily world beyond.
How One AI-Driven Media Platform Cut EBS Costs for AWS ASGs by 48%

But as business has evolved so too the network perimeter has dissolved. Fixed locations have given way to mobile users, corporate applications to cloud services, and servers to cloud instances. Security threats have skyrocketed, and so have our security appliances. No longer is there a safe corporate network and dangerous Internet – there is only the network.
This development offers a unique set of challenges for enterprises, especially larger, international companies which have office branches in different countries.
Legacy SD-WAN challenges
Legacy WAN architectures based on MPLS services do a solid job providing predictable performance between offices, but they’re not implemented in a way that easily accommodates the new realities facing IT. Mobile users connect to the Internet through VPNs and firewalls not the MPLS service. Access to cloud services is across the unpredictable, unsecure Internet not MPLS. And users are consuming ever more bandwidth, an expensive resource for MPLS networks.
Key legacy WAN cons include:
Inflated bandwidth costs. Anyone who’s purchased MPLS bandwidth for their business and Internet DSL for their home has endured the surreal experience of paying 3-times or even 10-times more per megabit for MPLS bandwidth. But as Internet performance has improved and bandwidth-intensive Internet-and cloud-bound data flows has become the norm, IT leaders are questioning why should keep on spending significant budget on WAN bandwidth.
Degraded cloud performance. Backhauling Internet traffic can also result in the “trombone effect”: when Internet traffic is pulled back to the centralized portal only to be sent onto the Internet for a destination near the sending user. When Internet sites or cloud resources sit near or within the path to the Internet destinations, the performance impact of “tromboning” is usually nominal. However, when a portal is out-of-path or far away from the destination, latency increases significantly.
Limited agility. Less pronounced, but perhaps equally important, is the rigidity of MPLS services and conventional IP routing. The WAN is fragmented, treated as individual locations and resources. There is typically no centralized control for configuring locations or deploying new applications.
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN brings unparalleled agility and cost savings to networking. With SD-WAN, organizations can deliver more responsive, more predictable applications at lower cost in less time than the managed MPLS services traditionally used by the enterprise. IT becomes far more agile, deploying sites in minutes; leveraging any available data service such as MPLS, dedicated Internet access (DIA), broadband or wireless; and being able to reconfigure sites instantly.
SD-WAN does this by separating applications from the underlying network services with a policy-based, virtual overlay. This overlay monitors the real-time performance characteristics of the underlying networks and selects the optimum network for each application based on configuration policies.
Where software-defined networking (SDN) deployed in a service provider network enables flexible deployment and usage-based solutions between high capacity sites (like headquarters and data centers) SD-WAN services help optimize traffic flows for performance and cost at branch sites.
By replacing traditional branch routers with appliances that assess and utilize different transport technologies based on their performance, it allows enterprises to route large portions of their traffic over cost-effective services, such as broadband.
Research firm Gartner has defined an SD-WAN as having four required characteristics:
- The ability to support multiple connection types, such as MPLS, frame relay and higher speed LTE wireless communications
- The ability to do dynamic path selection, for load sharing and resiliency purposes
- A simple interface that is easy to configure and manage
- The ability to support VPNs, and third party services such as WAN optimization controllers, firewalls and web gateways
SD-WAN benefits
SD-WANs reduce bandwidth costs by leveraging inexpensive services, such as Internet broadband, whenever possible. They can still use dedicated Internet access (DIA) for higher uptime and performance. (DIA is often more expensive than broadband but less than MPLS and comes with some service guarantees.)
The main goal of SD-WAN (SDWAN) technology is to deliver a business-class, secure, and simple cloud-enabled WAN connection with as much open and software-based technology as possible.
Companies are rapidly adopting SD-WAN technology because of the comprehensive financial and operational benefits it offers:
- Lowers WAN OpEx and CapEx costs, and overall total cost of ownership
- Provides greater business agility and responsiveness to keep pace with IT innovations
- Supports multiple, secure, high-performance connections eliminating backhaul penalties imposed by MPLS networks
- Allows for load sharing across connections and adjusts traffic flows based on network conditions to improve performance
- Supports the automated provisioning of – and changes to – premium network services, such as VPNs, firewalls, security, WAN optimization, and application delivery control
- Supports zero-touch provisioning (ZTP)
- Improves network security by encrypting WAN traffic and segmenting the network to minimize damage if breaches occur
SD-WAN limitations
Though SD-WAN brings many benefits, there are also key limitations. Extending the SD-WAN to the cloud requires installing an SD-WAN in or near the cloud provider’s data center, a complicated if not impossible task. SD-WAN completely ignores mobile users.
And while traffic is encrypted, exposing branches to the Internet raises the threat of malware, phishing emails, and other attacks. Deploy security appliances at the branch means that continuing with the costs of purchasing, sizing, and maintenance associated with security appliances continues.
Overcome these limitations by using a cloud-based SD-WAN
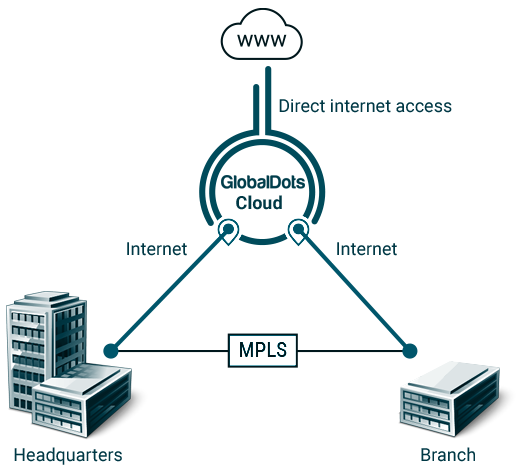
The emerging solution to these limitations is to converge security and networking functions together into cloud-scale software. All Internet and WAN traffic is sent to and received from the provider’s point of presence (PoP) running the software. PoPs, in turn, communicate over their own backbone, avoiding the performance problems associated with the Internet core.
The important point is that the challenges of running both networking and security stacks at the branch office are alleviated. The SD-WAN devices in this case form from a “thin edge” with minimal processing.
SD-WAN moves all security, traffic steering and policy enforcement into a multi-tenant cloud service built on a global, privately-managed network backbone.
To solve all problems and limitations related to legacy WANs and SD-WANs, GlobalDots has developed the GlobalDots Cloud – a secure, cloud-based emterprise network which connects all business resources including data centers, branches, mobile users and cloud infrastructure into a unified network.
Conclusion
While legacy WAN has had its place as a business solution, it’s no longer viable due to increased costs, degraded cloud performance and limited agility. SD-WAN is a better option, but it also has limitations like security issues and no integration for mobile users.
GlobalDots offers a solution that helps enterprises have all the advantages of a SD-WAN, without the limitations. It’s a secure, cloud-based SD-WAN as a service with built-in global backbone and integrated security.
With GlobalDots, WAN transformation will not merely end in MPLS cost avoidance. It will present a full roadmap for streamlining the networking and security infrastructure of the organization.
If you have any questions about how we can help you connect all your business resources and data centers into a secure, unified network, contact us today to help you out with your performance and security needs.






