Sandvine and PeerApp Collaborate to Demonstrate Virtualized Content Caching Solution
PeerApp, the developer of Internet content caching technologies and the creator of award-winning UltraBand transparent caching solution, announced that it would be collaborating with broadband solution providers Sandvine and Dell to showcase the Industry’s First Virtualized Content Caching Solution at IDF 2014. The IDF or the Intel Developer Forum was held at San Francisco from September 9-11 and the Companies showcased the joint solution at Dell’s Booth #920.
This joint solution would leverage PeerApp’s UltraBand caching engine with Sandvine’s patented application-specific Divert solution that runs on virtual machines that are powered by Dell’s hardware. The blend of solutions creates Network Functions Virtualization, enabling service providers to quicky build and deploy dynamic, virtualized networks that meet their requirements.
How One AI-Driven Media Platform Cut EBS Costs for AWS ASGs by 48%

Read the full story at CDN Advisor.
How to evaluate a DDoS mitigation solution
IDG Research found that it takes an average of 10 hours before a company can even begin to resolve an attack. On average, an attack isn’t detected until 4.5 hours after its commencement and typically an additional 4.9 hours passes before mitigation can commence.
With outage costs averaging $100,000 per hour, it means that a DDoS attack can cost an Internet-reliant company $1 million before the company even starts to mitigate the attack. Like any web security solution, a mitigation solution must fit your business requirements, as well as protect your IT infrastructure. Akamai’s free eBook “Threats and Mitigations: A Guide to Multi-Layered Web Security” covers all the key points of web safety. When it comes to building a strong DDoS mitigation defense you can’t rush into the first solution that is returned by a search engine.
You can download the eBook for free at Akamai.
Check the article at Akamai Blog.
Dyn Releases Two New Mobile Apps
Dyn, the Internet Performance firm announced the release of two new mobile apps, available for Android and iPhone. Dyn WHOIS and Dyn Dig, have already been downloaded more than 30,000 times and are available for free in the iTunes store and Google Play.
Dyn WHOIS is a utility that allows users to query the global and many country code WHOIS servers for the domain name contact information. The information can be used to find the individuals or entities responsible for the registration of a domain, as well as the registration and expiration times of the desired domain.
Dyn Dig is a utility application that allows users to query a specified DNS server or their carrier’s DNS servers for public DNS records. In the records, users can find information such as the domain’s actual IP address along with the authoritative servers for that domain. The apps mark the first phase of Dyn’s mobile strategy, that will soon evolve into the company’s core product areas. Additional tools are also in development.
Check the full story at Dyn Blog.
Graphene And The Internet of Things
In 2013 the European Union’s Future and Emerging Technologies or FET announced its $2.3 billion grant. The mission of the program was to enhance new technological solutions based on graphene. The program aimed to promote high-risk research in the field of high technologies. All the expected discoveries will be a breakthrough in Cloud Computing and Internet of Things.
Graphene is a super-material that can actually provide a new approach and value to everything that modern high technologies own these days. Graphene, as compared to silicone (a super-material for electronics), doesn’t possess an “energy gap”, and cannot be turned on/off. We’ll be granted an opportunity to enjoy surprisingly thinner high tech items of unmatched power. This can be true of both super-light conductors and unbelievably powerful world’s processors. The angle of faster processors will mean faster deliverability of data from the Computing and into the Cloud. Graphene’s unique properties include conductivity, strenght, flexibility, transparency and it’s two dimensional (each layer is one atom thick, giving a unique electrical and computing properties). Like plastics, graphene could potentially be used in a broad variety of materials and situations.

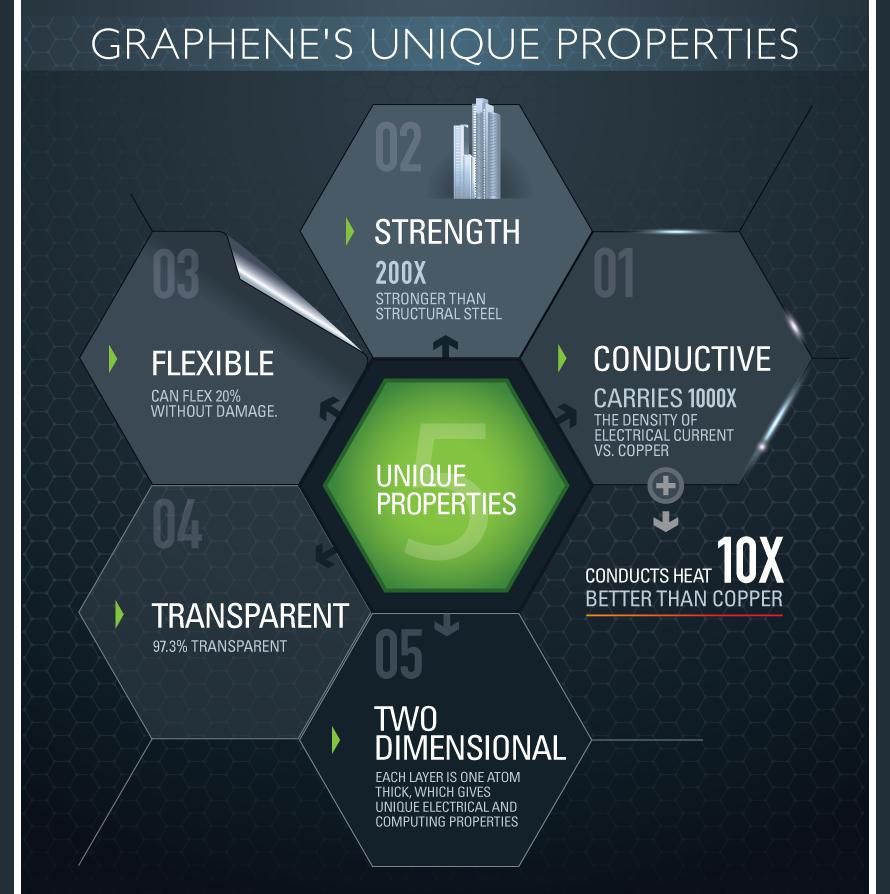
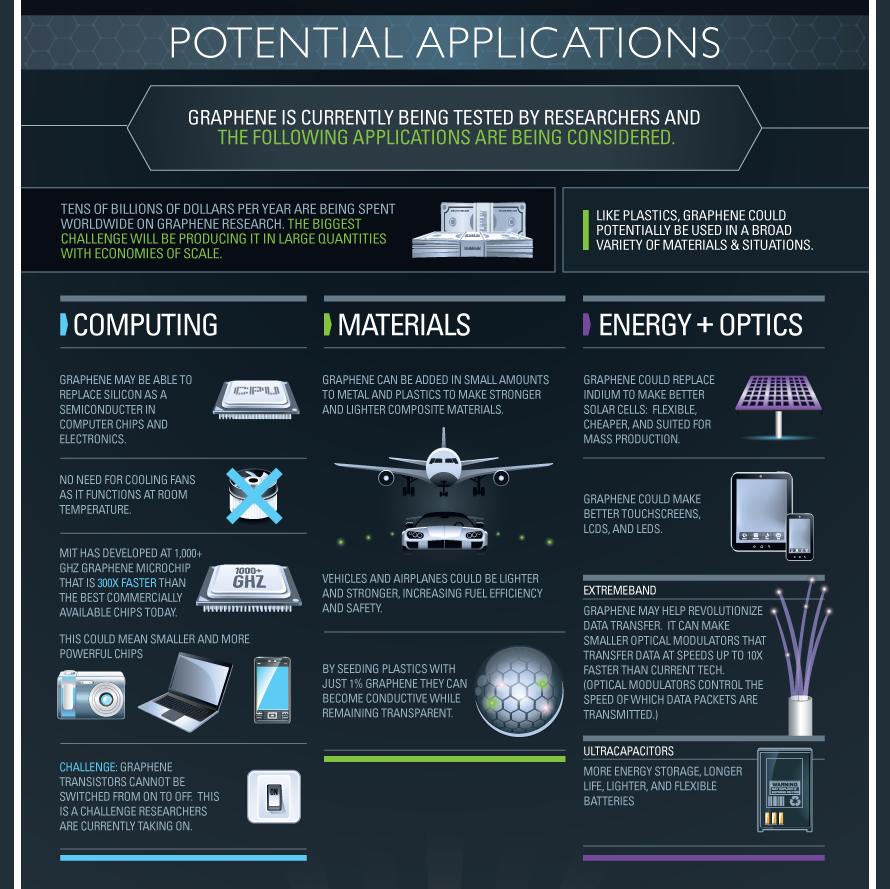
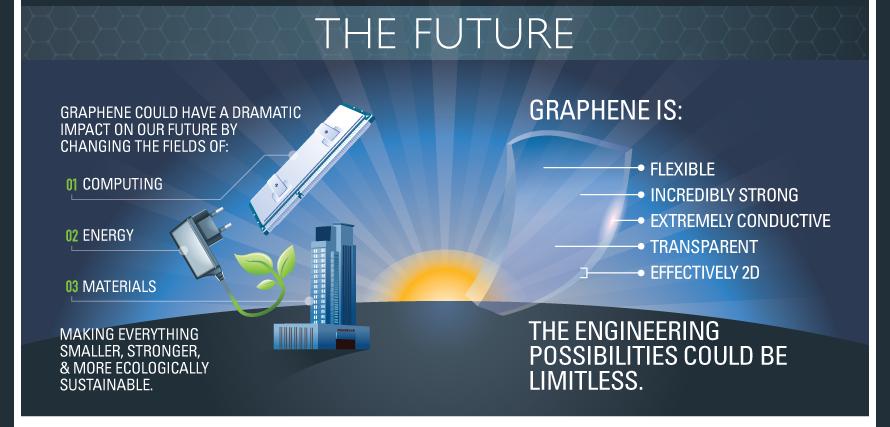

For the full story, go to CloudTweaks.
Emerging Threats In Cyber Security
Businesses today have to deal with a huge variety of threats from the Internet. Even relatively savvy managers may be falling behind as the advent of cloud computing revolutionizes the security needs of online data. As reported by the non-profit Cloud Security Alliance, cloud computing poses several risks that traditional security strategies don’t account for. In particular, the cloud allows for a level of anonymity that attackers can capitalize on in their efforts to avoid detection.
The Cloud Security Alliance announced a competition in which hackers are invited to try and beat the new security software. The results of that competition, which offers a $10,000 top prize, will reveal a lot about the best practices and products in online security. The most common internet attack methods are: eavesdropping (interception of communications by an unauthorised party), trojans (appearing as benign programs, but actually have a malicious purpose), viruses ( self-replication programs that use files to infect and propagate), worms (mass mailing worms or network-awake worms, infecting targets or other computers), phishing, Denial of Service (most commonly used to bring down web sites) and IP Spoofing Attacks.Encrypting your data is essential for protecting sensitive data and preventing data loss due to theft or equipment loss. Use digital certificates to sign all of your sites and implement DLP and auditing.
Read the full article at CloudTweaks.







