Websites present a lucrative opportunity for hackers. Business websites which deal with money and sensitive information are especially at risk of cyber-attacks. Malicious actors can use a myriad of attack options to steal sensitive corporate data, trick end users into revealing personal information, or simply temporary disable a website.
Even a small-scale attack which does relatively little damage (let’s say, brings down a website for couple of hours), can have a huge negative impact – a large ecommerce website can lose millions in revenue, and its reputation will be ruined.
How One AI-Driven Media Platform Cut EBS Costs for AWS ASGs by 48%

Besides the dangers of a data breach itself, there is also the risk of reputation and credibility loss to those who fall prey to an attack on their web site security. In addition, a hacker’s motivations are becoming not only financial, but also political. Overall, hackers can be hugely damaging to a business or institution. Unless web site security is a continuous effort, your organization could become the target of malicious attacks.
Malicious software, which is used to infect websites, gather data and in some cases even hijack computer resources. A site where an attacker has gained an access to can be used to redirect traffic, infect visitors with unwanted software and lately even to use the visitor’s computer resources to mine untraceable cryptocurrencies.

A web security issue is faced by site visitors as well. A common web site attack involves the silent and concealed installation of code that will exploit the browsers of visitors. Your site is not the end target at all in these attacks. There are, at this time, many thousands of web sites out there that have been compromised. The owners have no idea that anything has been added to their sites and that their visitors are at risk. In the meantime visitors are being subject to attack and successful attacks are installing nasty code onto the visitor’s computers.
Google and other search engines warn your customers and restrict them from entering your website. Lately, Google, for example, has stepped up the game even more. Starting from July 2018, every website without SSL (HTTPS) is marked as insecure and therefore receive an SEO penalty. This makes it harder for your company to reach to new customers.
Some companies invest a lot of time and money into a website on the hope they’re never targeted by cyber criminals. This approach is risky, especially nowadays, when over 4000 cyber-attacks occur daily.
Cyber-criminals constantly scour the inter, looking for an easy victim. Organizations which fail to perform basic web security measures risk having their business severely hurt by some form of a cyber-attack.
Simply put, your website security matters.
How to secure your website
Securing your entire website from all possible attacks is almost impossible without help from cyber-security experts.
Still, there are some measure everyone can take to prevent basic cyber-attacks.
Update your website regularly
Websites are apps and apps need updates! Your website is an application that needs to be updated regularly to be secure against threats.
For example, the following elements should always be kept up-to-date:
- The OS of the server on which your website is hosted
- The CMS on which your website may have been designed
- Any third-party app associated with your website
It may seem obvious, but ensuring you keep all software up to date is vital in keeping your site secure. This applies to both the server operating system and any software you may be running on your website such as a CMS or forum. When website security holes are found in software, hackers are quick to attempt to abuse them.
If you are using a managed hosting solution then you don’t need to worry so much about applying security updates for the operating system as the hosting company should take care of this.
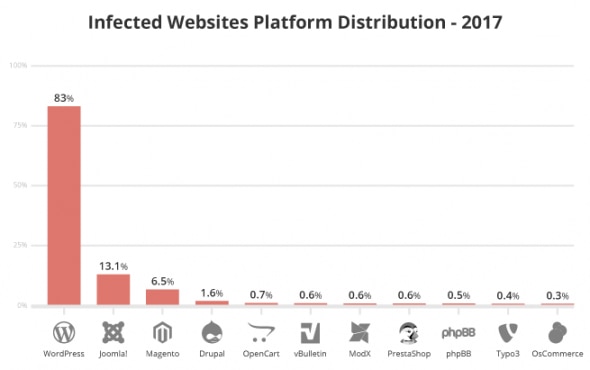
According to this report by Sucuri, WordPress is the most infected CMS platform (2017 data).
Use secure communication protocol (SSL)
This is crucial for website security and should be done immediately! Secure communication protocol – https – ensures your website interacts with others sites, users, applications, etc., in a secure way – using SSL encryption – without any data compromise.
The principal motivation for HTTPS is authentication of the accessed website and protection of the privacy and integrity of the exchanged data while in transit. It protects against man-in-the-middle attacks. The bidirectional encryption of communications between a client and server protects against eavesdropping and tampering of the communication.
In practice, this provides a reasonable assurance that one is communicating without interference by attackers with the website that one intended to communicate with, as opposed to an impostor.
Test your website for security vulnerabilities
Any website security would be incomplete without this step, which is also known as penetration testing. Pen testing, for short, is the practice of testing a system or application for security weaknesses that a hacker could exploit.
This is also known as website or web application penetration testing. Here you employ a group of trained professionals – known as ethical hackers – to test your website security. These people understand the weak points of your website very well and by testing them, make your website strong enough against various security attacks.
Some of the tests they perform include:
- Application login testing
- Contact form testing
- Credential encryption testing
- User session testing
- Testing against popular website attacks
Check your passwords
Using strong passwords is a must, but people often forget to do it. Strong passwords are usually a minimum of eight characters, containing at least one uppercase letters and a number.
You should set strong passwords for your servers and admin area, but also try to enforce a security rule among your employees to use strong passwords. Passwords should always be stored as encrypted values, preferably using a one way hashing algorithm such as SHA. Using this method means when you are authenticating users you are only ever comparing encrypted values.
Validate on both sides
Validation should always be done both on the browser and server side. The browser can catch simple failures like mandatory fields that are empty and when you enter text into a numbers only field. These can however be bypassed, and you should make sure you check for these validation and deeper validation server side as failing to do so could lead to malicious code or scripting code being inserted into the database or could cause undesirable results in your website.
Conclusion
A website is a crucial digital asset for any modern company. As such, it should be protected against malicious actors who target websites with cyber attacks. Website security is a complex process, but in this article we have distilled the basic measure anyone can take to reduce the chance of being hit by a crippling cyber-attack.
If you want to make sure your website or application is completely protected against all possible cyber threats, contact us today to help you out with your performance and security needs.






